Structural Stability
Structural Audit In Delhi- GurgaonOld buildings/structures have reduced strength in the due course of time. If further use of such weakened structures is continual, it may endanger the lives of the occupants and surrounding occupancy. Appropriate actions need to be applied to improve the performance of structures and restore the desired function of structures. Thus, it is of utmost importance to perform a structural audit of existing buildings and to implement maintenance/ repair work time which will lead to prolonged life of the building and safety of the occupant. A structural Audit is an overall health and performance checkup of a building like a doctor examines a patient. It ensures that the building and its premises are safe and have no risk. It analyses and suggests suitable repairs and retrofitting measures required for the buildings to perform better in their service life.
Components of a Structural Audit
-
Visual Inspection: A thorough examination of both the exterior and interior of the building to detect visible signs of damage, such as cracks, water seepage, and corrosion.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic pulse velocity tests, rebound hammer tests, and infrared thermography are used to assess the structural integrity without causing damage to the building.
-
Load Analysis: Evaluation to determine if the building’s current load exceeds its designed capacity, crucial for buildings with changes in usage or additional floors.
The Structural Audit Process
-
Preliminary Assessment: Collecting basic information about the building, its history, and any known issues.
-
Site Visit and Inspection: Conducting a detailed on-site inspection to identify immediate concerns and gather data.
-
Testing and Analysis: Performing necessary tests and analyses to evaluate the structural integrity and material properties.
-
Evaluation and Risk Assessment: Analyzing the data to assess the building’s current state and any associated risks.
Why Choose Us?
- Expertise: Our team comprises seasoned professionals with extensive experience in structural engineering and audits.
- Advanced Technology: We employ state-of-the-art tools and techniques for precise assessments.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Our detailed reports provide clear insights and actionable recommendations.
- Customer Focused: We prioritize our clients' needs and safety, ensuring a thorough and reliable service.
Benefits of Regular Structural Audits
- Early Detection of Problems: Identifying issues before they become severe helps in avoiding costly emergency repairs.
- Enhanced Safety: Ensuring the building is safe for occupants and nearby structures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting local building codes and standards.
- Extended Building Life: Prolonging the functional life of the building through timely maintenance and repairs.
Purpose of Structural Audit :
- To save human life and buildings
- To understand the condition of building
- To find critical areas to repair immediately
- To comply with statutory requirements
- To enhance life cycle of building by suggesting preventive and corrective measures like repairs and retrofitting.


Purpose of Structural Audit
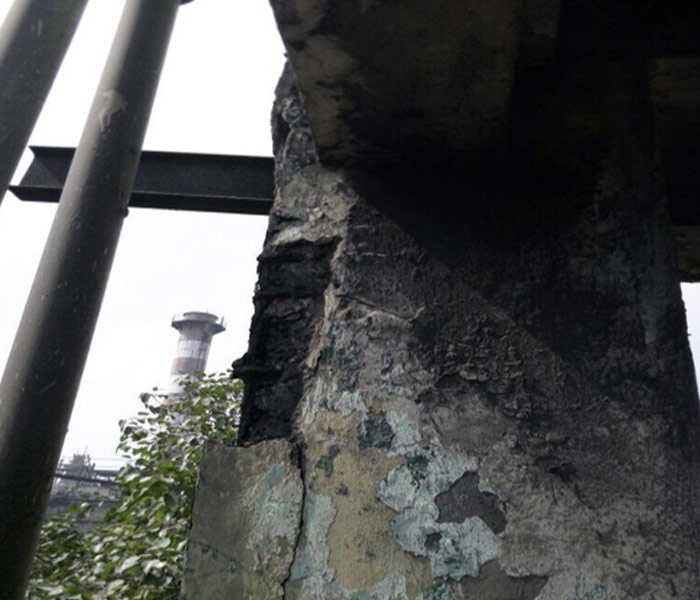

Visual Inspection
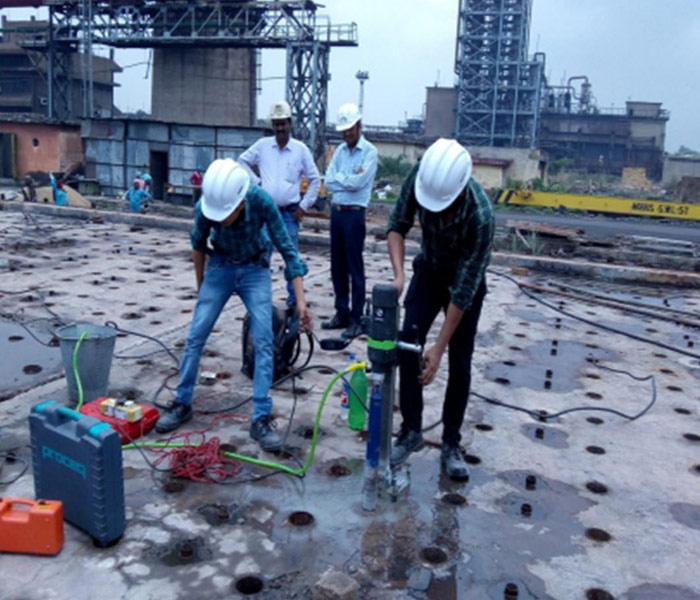

Core Test
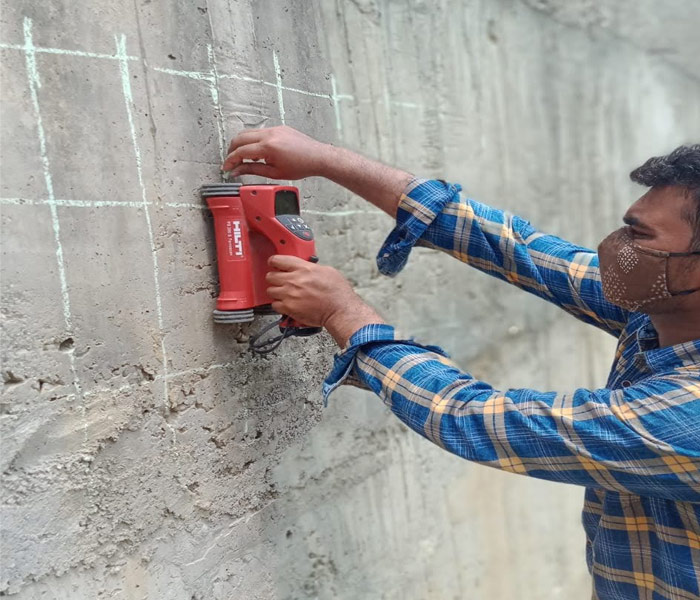

RCC Scanning

Chemical Test
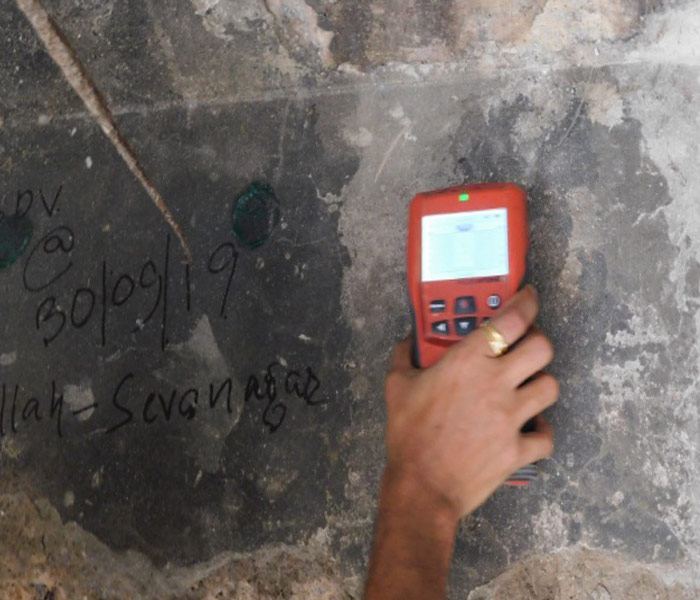

Cover Meter Test
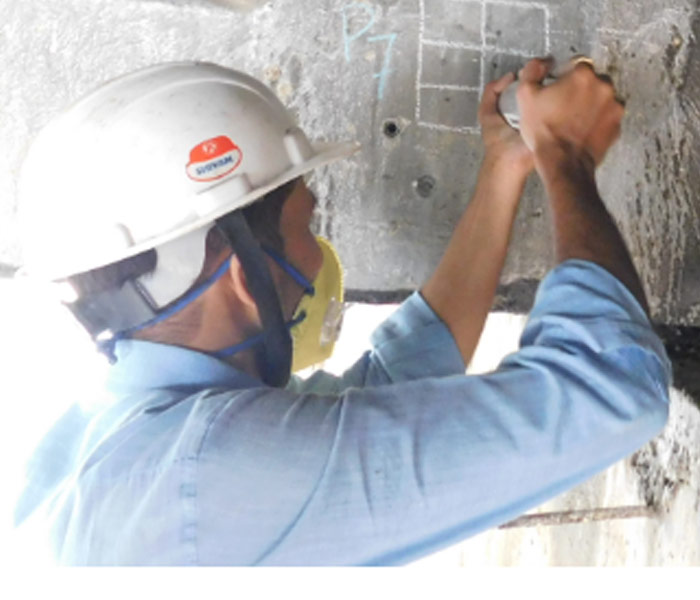

Rebound Hammer Test
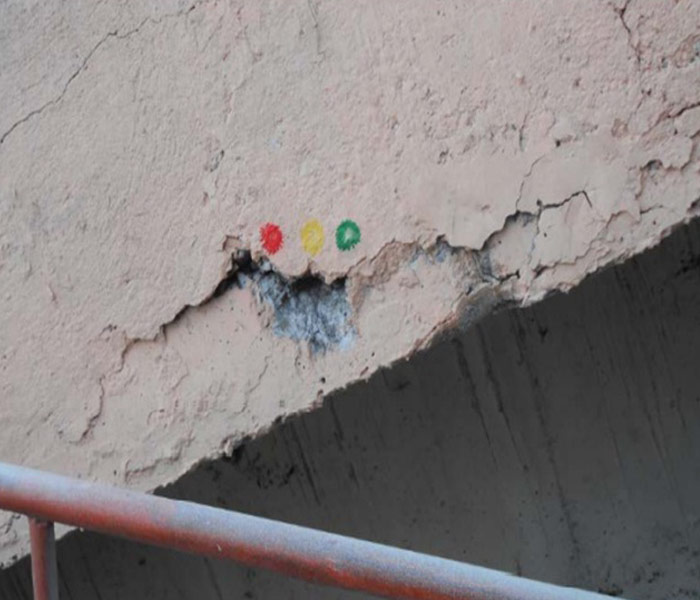

Hammer Rap Survey
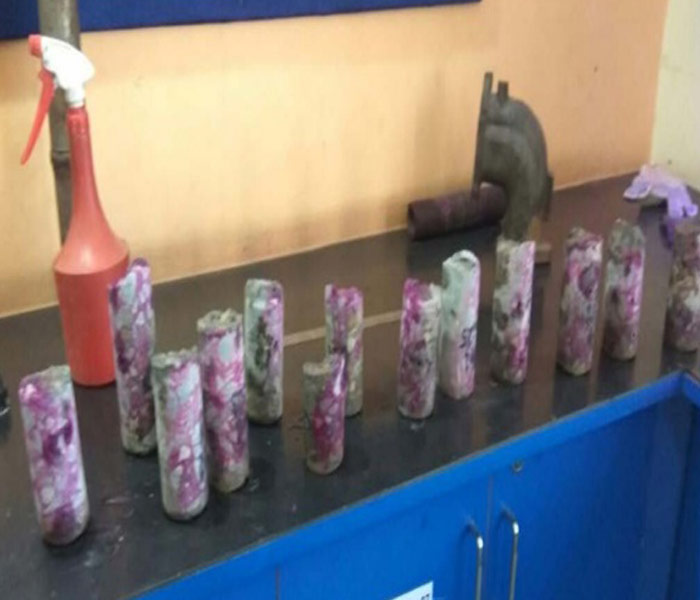

Carbonation Test